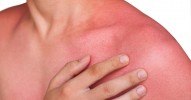
The risk of ringworm and itching increases in summer
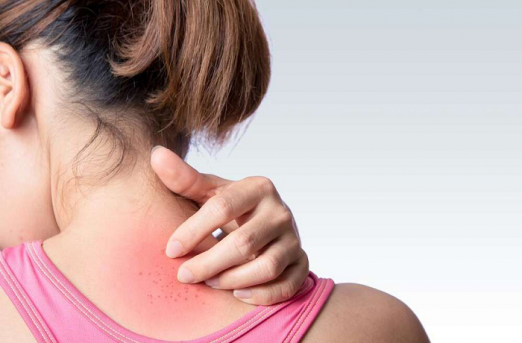
April 3, Kathmandu.In summer, skin diseases like ringworm and itching are more common. The most common problem among these is fungal infection. This infection spreads rapidly due to humidity, dust and sweat in summer. This causes problems like itching, redness and burning on the skin.
If these problems are ignored, the situation can become serious in some cases. People who spend more time outside in summer or are troubled by sweating are also at greater risk of fungal infection.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), every year around 1 billion people in the world get fungal infection. Out of these, 10-2 billion people have serious problems. Whereas, several lakh people even die. Now the risk is higher in the summer season.
What is fungal infection?
Fungal infection is a type of infection caused by fungus. Fungi are microorganisms that can cause infection inside or outside our body.
Why do fungal infections increase in summer?
Dr. says that the risk of fungal infection increases due to excessive dust and sweat in summer.
What are the symptoms of fungal infection?
Fungal infections usually cause itching. This can cause swelling and redness in the affected areas.
How contagious can a fungal infection be?
Fungal infections can be contagious, but how contagious it will be depends on the type of infection and the affected area. Some fungal infections can easily spread to others, while some are less contagious.
Skin infection: It can easily spread from an infected person to others. Coming in contact with an infected person or walking on a wet surface can cause the infection.
Fungal nail infection: This can also spread from one person to another, especially through contact with someone's infected nails.
Fungal hair infection: This is also highly contagious and can spread through direct contact or through comb, towel.
Candida infection: Candida is a common fungal infection that usually occurs in the mouth, private parts or intestines. It is less likely to spread from one person to another, but it can spread easily in people with a weakened immune system.
Fungal infections of the respiratory tract: Some fungal infections such as Aspergillus, which are airborne, can spread through the respiratory tract. These do not usually affect healthy individuals.
What is the treatment for fungal infection?
The treatment of fungal infection depends on its severity and type. For mild infections, some antifungal creams or ointments are enough. In severe cases, when the infection spreads to the internal organs, antifungal medicines like fluconazole or itraconazole are given. Also, cleanliness is advised.
What effect does our diet have on fungal infections?
Our diet has a direct impact on fungal infections. Eating too much sugar and refined carbohydrates can increase fungal infections, especially Candida. A diet rich in fiber and protein strengthens the immune system. Such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains and protein.
Probiotics like yogurt help control fungal infections. Vitamins C and D boost immunity, allowing the body to fight infections. Drinking enough water keeps the body hydrated and flushes out toxins. This type of diet helps in both prevention and treatment of fungal infections.
Do scars remain on the skin after the fungal infection is cured?
After a fungal infection is cured, there may be marks on the skin, such as pigmentation and scars. This may be due to the severity of the infection, itching, or lesions. To reduce these marks, keep the skin moisturized, avoid the sun, and use home remedies such as lemon or vinegar. Medical creams may also help. If the marks are severe, consult a skin specialist.
Which habits should be changed to avoid fungal infection?
To avoid fungal infection, some important habits should be learned. These habits will not only help prevent infection but will also keep your skin and health better:
Keep yourself clean: Bathe daily and keep your body dry, especially wet and sweaty areas, such as the armpits, legs, and inner thighs.
Avoid wearing wet clothes: Change your clothes immediately after swimming or sweating, as wet skin is ideal for fungal infections.
Don't wear someone else's clothes: Don't share towels, shoes, combs or clothes with anyone else.
Avoid wearing synthetic clothes: Synthetic clothes do not allow air to pass through the skin and retain moisture, which can cause fungus to develop. So wear cotton clothes.
Keep your immunity strong: Eat a healthy diet, exercise regularly and get enough sleep. This will keep your immune system strong.
Pay attention to irritation or itching: If there is any rash, itching or redness on the skin, do not ignore it and consult a doctor immediately.
Share this with your friends:
प्रत्येक महिला पुरुषभन्दा कमजोर छैनन् : कमला भासिन
 नरेश ज्ञवाली ►
भदौ २७, काठमाडौं। दक्षिण एसियामा लैङ्गिक समानता, शिक्षा, गरिबी निवारण, मानवअधिकार र शान्तिका...
नरेश ज्ञवाली ►
भदौ २७, काठमाडौं। दक्षिण एसियामा लैङ्गिक समानता, शिक्षा, गरिबी निवारण, मानवअधिकार र शान्तिका...
पुरुष कलमले पूर्ण नारीलाई लेख्न सक्दैन
 काठमाडौं। मान्छेहरू कडा भएर बोलेको भन्दा नरम भएर बोलेको मनपर्छ । खरा कुराभन्दा नरम, सरस र सलिल कुराहरू मनपर्छ । तर...
काठमाडौं। मान्छेहरू कडा भएर बोलेको भन्दा नरम भएर बोलेको मनपर्छ । खरा कुराभन्दा नरम, सरस र सलिल कुराहरू मनपर्छ । तर...
कालो तिलले कम्मर दुखेको र अनुहारमा भएको पोतोको उपचार गर्छ
 काठमाडौं । कालो तिल अथवा तिलबाट प्राप्त हुने बिऊ तेल उत्पादनको लागि प्रयोग गरिन्छ । अनुहारमा चायाँ, पोतो वा दाग,...
काठमाडौं । कालो तिल अथवा तिलबाट प्राप्त हुने बिऊ तेल उत्पादनको लागि प्रयोग गरिन्छ । अनुहारमा चायाँ, पोतो वा दाग,...
दुबईमा पहिलो पटक नेपाली कल्चरल पहिरनको फेसन शो सम्पन्न
 काठमाडौं। गत माघ २८ गते दुबईमा नेपाली कल्चरल पहिरनको फेसन शो पहिलो पटक फेसन फ्युजन २०१७ सम्पन्न भयो । एनआरएन...
काठमाडौं। गत माघ २८ गते दुबईमा नेपाली कल्चरल पहिरनको फेसन शो पहिलो पटक फेसन फ्युजन २०१७ सम्पन्न भयो । एनआरएन...
उमेर अनुसारको हुनुपर्छ खान्की, अनि मात्र मानिस स्वस्थ रहन्छ
 काठमाडौं। पोषणको आवश्यकता उमेरअनुसार परिवर्तन हुन्छ । उमेरको हरेक अवस्थामा स्वयंलाई स्वस्थ राख्न शरीरलाई...
काठमाडौं। पोषणको आवश्यकता उमेरअनुसार परिवर्तन हुन्छ । उमेरको हरेक अवस्थामा स्वयंलाई स्वस्थ राख्न शरीरलाई...
मुलुकका सम्मानित पदमा महिलाको उपस्थिति, सबैका लागि आशाको ढोका उघारे
 काठमाडौं। अहिले नेपालका तीनवटै अंगका प्रमुख महिला भएकाले नेपाली राजनीतिक क्षेत्रमा मात्र नभएर सामाजिक...
काठमाडौं। अहिले नेपालका तीनवटै अंगका प्रमुख महिला भएकाले नेपाली राजनीतिक क्षेत्रमा मात्र नभएर सामाजिक...
यी भोजन खाए छाला सुन्दर हुन्छ !
 काठमाडौं। स्ट्रबेरी : यो भिटामिन सीले भरपुर हुन्छ । भिटामन सीले छालालाई चाउरीबाट जोगाएर सधैं जवान राख्न मद्दत...
काठमाडौं। स्ट्रबेरी : यो भिटामिन सीले भरपुर हुन्छ । भिटामन सीले छालालाई चाउरीबाट जोगाएर सधैं जवान राख्न मद्दत...
लोग्नेमान्छेको जात केटी देखेपछि.....
 काठमाडौं । शान्ताको विवाह भएको पाँच वर्ष बितिसक्दा पनि छोराछोरी भएनन् बरु उनलाई एकाएक ब्लड क्यान्सर भयो । समयले...
काठमाडौं । शान्ताको विवाह भएको पाँच वर्ष बितिसक्दा पनि छोराछोरी भएनन् बरु उनलाई एकाएक ब्लड क्यान्सर भयो । समयले...
मनोसामाजिक समस्या के हो?
 साउन ११, काठमाडौं । मनोसामाजिक समस्या भन्नाले मन र समाज वीच हुने समस्या हो । यो जो कोही व्यक्तिलाई पनि हुन सक्छ ।...
साउन ११, काठमाडौं । मनोसामाजिक समस्या भन्नाले मन र समाज वीच हुने समस्या हो । यो जो कोही व्यक्तिलाई पनि हुन सक्छ ।...
महिलाको दोस्रो विवाहको कुरा सुन्दा पढेलेखेकैले अनुहार बिगार्छन्
 काठमाडौं। दोस्रो विवाहबारे मैले नसोचेको, नचाहेको होइन । तर, म मेरा आत्मीयसँग फेरि विवाह गर्नेबारे कुरा गर्छु,...
काठमाडौं। दोस्रो विवाहबारे मैले नसोचेको, नचाहेको होइन । तर, म मेरा आत्मीयसँग फेरि विवाह गर्नेबारे कुरा गर्छु,...